
Sauvignon Blanc

Cabernet is one of the most popular varietals in the world. It is truly the world’s most famous grape. It is a big, bold, dry red that most seem to enjoy!
Cabernet Sauvignon actually came from an accidental crossing of two other well-known varieties: Sauvignon Blanc and Cabernet Franc. What a wonderful accident! It is largely recognized in the Bordeaux region of France as well as California’s Napa Valley.
Yes, Cabernet is a pretty big deal. Want to know more about it?
The following guide will illustrate what Cabernet Sauvignon tastes like (aroma, flavor, and structure). It will also tell you where it’s from, provide you with common food recommendations, top producers, similar varietals, and let you know why you should be drinking more of it!!!
Not only in popularity, but in style! Cabernet Sauvignon is generally full-bodied and big in flavor. It’s often oaked, which can enhance this!
Cabernet Sauvignon is usually an “in your face” variety. It’s very structured with ripe dark fruit flavors. Also, it is typically higher alcohol compared to other red varieties.
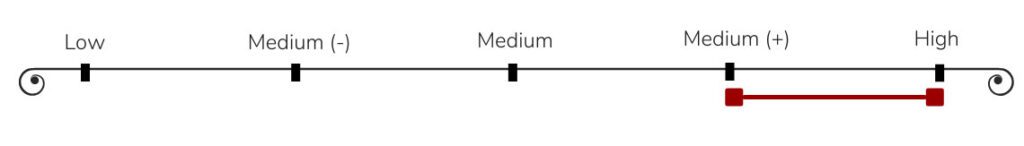
Cabernet Sauvignon is far from sweet. It also has a good amount of tannin (see chart below). It can be “grippy”.
STANDARD TASTING NOTES: These are your benchmark exam-style tasting notes.






ALTERNATIVE TASTING NOTES: These notes are less standardized, but can be personally associated with this variety.





These are the most familiar tastes and aromas I typically find in a glass of Cabernet Sauvignon. It’s also common to find raspberry, green pepper, violets, tobacco, coffee, and baking spices, depending upon where the wine is from, and how it is made. Remember, wine tastes are somewhat relative. There may be some different tasting notes you consistently find while drinking Cabernet Sauvignon.
There is no “one size fits all” when it comes to structure for every grape, however, there IS a general range when it comes to body, acid, alcohol, and tannin for each. Below are general guidelines for classic representations. Growing conditions and winemaking techniques can impact each of the following.
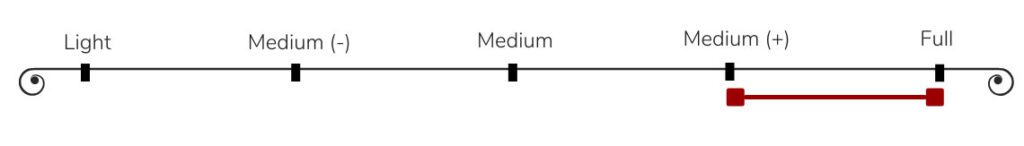
Think of that weight as a liquid scale, from water (light body) to heavy cream (full body) in your mouth. Cabernet Sauvignon is generally fuller than most red wines!
You can judge acidity based on weather your mouth waters after you take a sip of something. The more you salivate, the higher the acid. Cabernet Sauvignon has a good amount of acid, but its usually well balanced.
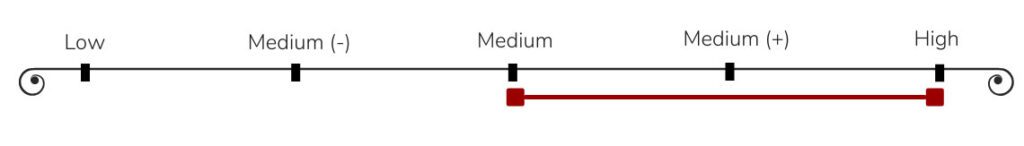
You can feel alcohol ‘burn’ the back of your throat when you take a sip. Cabernet Sauvignon is typically pretty high on the alcohol scale.
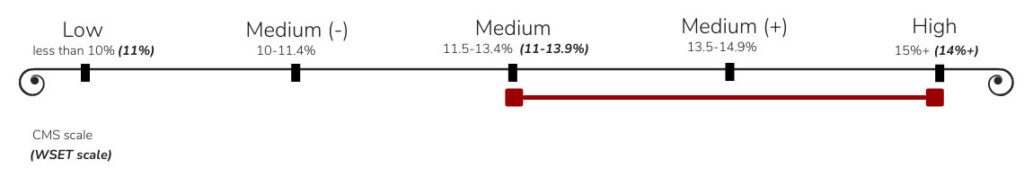
Tannin contributes to the dryness of a wine. It comes from the skin of the grapes during the winemaking process. You can tell a wine has high tannin if it dries out your tongue. It imparts almost a bitter flavor. Cabernet Sauvignon will show a good amount of this.
Primarily in Bordeaux (left bank)
Left Bank Bordeaux = Cabernet Sauvignon dominant blends. The bottle may be labeled with the regions Medoc, Haut Medoc, or Graves.
There are 6 Bordeaux varieties: Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Cabernet Franc, Petit Verdot, and Malbec. Most Bordeaux’s are a combination of the first three grapes. The Gironde River splits Bordeaux in half and the area left of the river produces wine made with a high percentage of Cabernet Sauvignon. Cabs from this area usually have less alcohol than in California and higher acidity. They are usually medium to full bodied with more earthy flavors than fruit flavors. You will taste a lot more tart berry, green pepper, and tobacco flavors in these wines.
Primarily in California and Washington
In 1976 a Cabernet Sauvignon from the Stags Leap district in Napa Valley beat out some of the top Château in Bordeaux. This is what put California on the map for quality wine and kick started the US wine industry. Different in style than French Bordeaux’s, California Cabernets are usually full bodied, fruity, big in alcohol, and often oaked with flavors of coffee, vanilla, and baking spices.
Washington Cabernet is usually a little more rustic in taste. Some red fruit qualities along with green pepper and spices.
You can also find wonderful Cabernet from Chile, Australia, Italy, and South Africa, among other areas!

Steak has such pronounced flavor, it is able to hold up to a bigger wine like a Cabernet. The flavors of both the food and wine complement each other. Also, because Cabernet is dry and tannic, a fattier cut of meat will help counter the dryness of the wine.

Cabernet is intense. Cheddar cheese is intense. So this pairing just works perfectly. (Cabernet can be hard to pair with cheeses that are aged or smoked…a mild white cheddar is usually a perfect match!)

Those savory rich flavors are what do it! Bonus points if you add cheddar cheese to the burger.
(common confusions)



↑ Some of the links above are Amazon affiliate links, which means that I will earn a commission if you choose to purchase them. I will never recommend anything that isn’t valuable or useful in my wine study journey, or something I have no experience with. I hope these products/resources are equally helpful in your wine journey.
No matter your current skill level, we can help you improve – pass that test, help your customers, impress your peers, gain trust and respect as a knowledgable and experienced wine professional.